Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Encuentre un especialistaIf you have irregular periods, unexplained weight gain, or excess hair growth, you may have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This hormonal imbalance affects millions of people, impacting the reproductive system and overall health. While there’s no cure, the right treatments can help manage symptoms and improve your well-being.

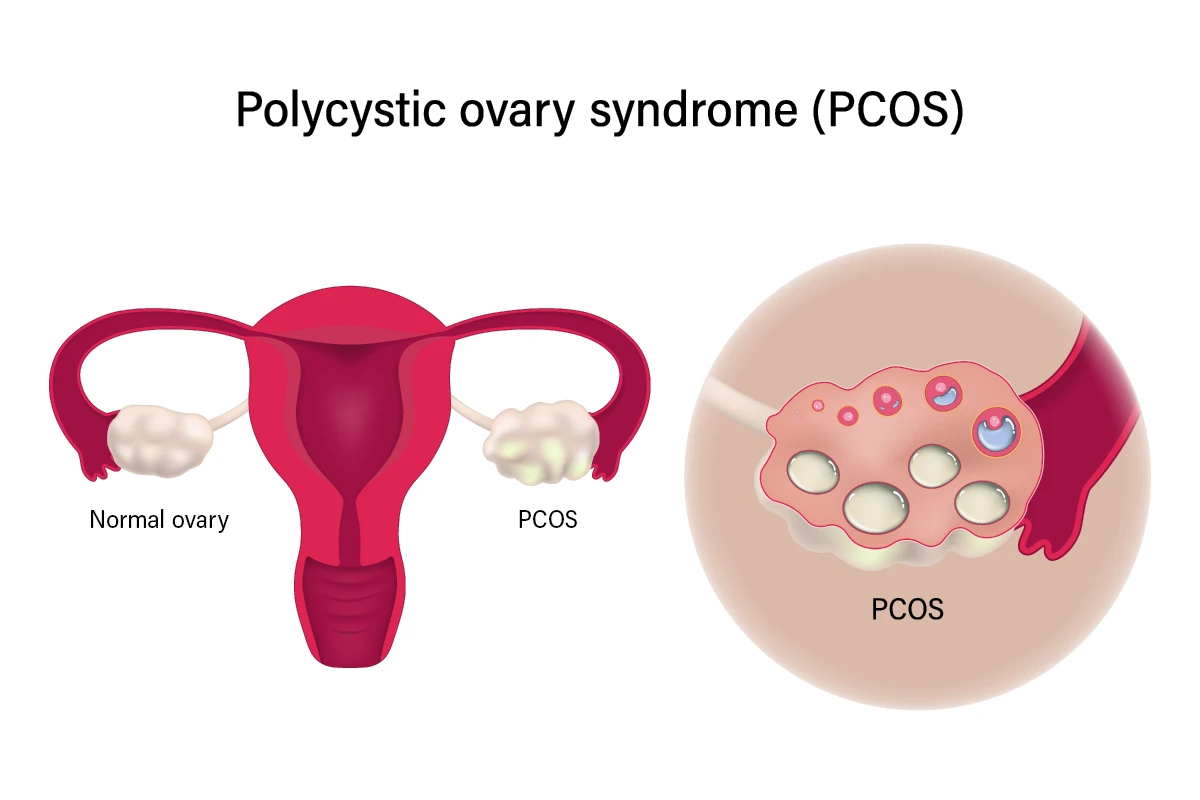
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that impacts your reproductive system, metabolism and overall health.
PCOS occurs when the ovaries produce excess hormones, leading to a hormonal imbalance that can cause ovarian cysts, irregular or missed periods and problems becoming pregnant.
Although the exact cause of PCOS is unclear, factors such as insulin resistance, abnormal hormone levels and adrenal gland dysfunction are believed to play a role in its development.
What hormones contribute to polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome disrupts the balance of several hormones. Key hormones involved with PCOS include:
- Androgens (male hormones): Elevated testosterone levels can cause acne, excess hair growth and hair thinning.
- Insulin: Many individuals with PCOS have insulin resistance, which causes your body not to use insulin properly and contributes to weight gain and increased testosterone production.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH): Higher-than-normal LH levels can interfere with ovulation, leading to fertility challenges.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Low FSH levels can disrupt egg development, making it more difficult to get pregnant.
- Progesterone: Insufficient progesterone can result in irregular or missed periods.
- Estrogen: While estrogen levels may remain normal or slightly elevated with PCOS, the hormonal imbalance can still disrupt your menstrual cycle and reproductive health.
Managing PCOS often involves addressing these hormonal imbalances through lifestyle changes and PCOS medication.
What are polycystic ovary syndrome symptoms?
PCOS symptoms vary, but the most common signs include:
- Acne and oily skin
- Dificultad para quedar embarazada
- Excess hair growth on the face and body
- Irregular or missed periods
- Skin darkening in specific areas
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
What worsens polycystic ovary syndrome?
Certain factors can make PCOS symptoms worse, including:
- Chronic stress: High cortisol levels can further disrupt hormonal balance.
- Desequilibrios hormonales: Issues with the adrenal glands or other endocrine disorders can make symptoms more severe.
- Insulin resistance: When the body struggles to use insulin effectively, it can lead to increased insulin levels, contributing to weight gain, excess hair growth, and acne.
- Lack of exercise: Regular physical activity helps regulate hormones, and a sedentary lifestyle may worsen PCOS.
- Poor diet: Consuming too many processed foods and refined sugars can cause blood sugar spikes, making PCOS symptoms worse.
- Weight gain: Excess weight, particularly around the midsection, increases insulin resistance and inflammation, intensifying PCOS symptoms.
Making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress and following your doctor’s treatment plan, can help alleviate PCOS symptoms.
How is polycystic ovary syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosing PCOS involves reviewing your medical history, symptoms and performing tests to measure hormone levels and ovarian health.
Since PCOS symptoms overlap with other conditions, your doctor may want to rule out other potential causes before confirming a PCOS diagnosis.
During an evaluation, your doctor may:
- Ask about menstrual cycle patterns, weight changes, and signs of excess hormones like acne or excess hair growth.
- Order blood tests to check hormone levels, blood sugar and cholesterol.
- Perform an ultrasound to examine the ovaries for cysts and assess the uterine lining.
Can polycystic ovary syndrome contribute to other health conditions?
If left untreated, PCOS can contribute to other conditions, including:
- Ansiedad
- Depresión
- Endometrial cancer
- Esteatosis hepática (hígado graso)
- Enfermedad cardíaca
- Apnea del sueño
- Diabetes tipo 2
Can you still get pregnant if you have PCOS?
Yes, it is possible to get pregnant with PCOS, but fertility challenges due to irregular ovulation may make conception more difficult. However, many individuals successfully conceive with the right approach. Strategies to improve fertility include:
- Fertility treatments: Options like intrauterine insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), and ovarian drilling may be recommended.
- Cambios en el estilo de vida: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and exercising can regulate hormones and improve ovulation.
- Medicamentos: PCOS medication such as ovulation stimulants and birth control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Stress management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and adequate sleep can support hormonal balance.
While PCOS can present challenges, many individuals go on to have successful pregnancies. If you’re trying to conceive, speak with your doctor about PCOS treatment options.
Polycystic ovary syndrome treatments & medications
While there is no cure for PCOS, treatment focuses on symptom management and overall health improvement. El médico puede recomendar:
- Birth control pills to help regulate hormone levels and menstrual cycles.
- Medications to balance hormones and support ovulation.
- Lifestyle changes to help you lose weight and improve symptoms.
- Insulin-sensitizing medications to manage insulin resistance in individuals with PCOS.
Reciba atención
Le ayudamos a vivir bien. Podemos ayudarle en persona o en línea.